According to the World Trade Organization (WTO), trade finance is a critical tool for facilitating trade transactions, accounting for 80 to 90 percent of the global trade. Moreover, trade finance not only streamlines international trade transactions but also supports global financial stability and efficiency.
Basically, trade finance is a range of financial instruments or methods accustomed to supporting and enabling international trade transactions. Otherwise, it is a means to lower the risks involved with global trade by filling the gaps between the needs of exporters (sellers) for prompt payment and the demands of importers (foreign buyers) for deferred payment until goods delivery.
Trade finance is essential for trade, which supports 25 percent of merchandise trade (WTO), which aims at addressing the risks related to cross-border payments and timing. In the absence of trade finance global, goods might not be able to cross borders as international deals are either too risky or too complicated to undertake, posing a negative effect on global economic growth and development.
Overall, trade finance not only finances a single transaction but also propels whole supply chains and industries. By financing the necessary facilitation of cross-border trade, it assists businesses to expand their operations, enter new niche markets globally, and fuel economic development on the global scale.
Generally, trade finance encompasses financial components, which is crucial for businesses to enhance trade transactions effectively. The following are the primary tools utilized in this financial practice:
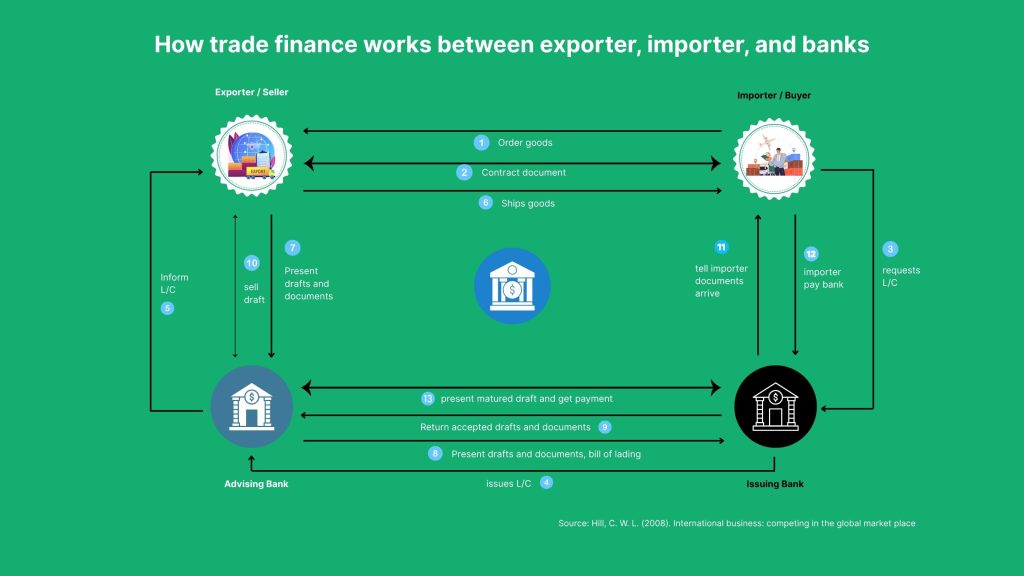
Indeed, letters of credits are one of the most widely used and versatile instruments in global trade. An L/C is a contractual document issued by a bank on behalf of the buyer (importer) which:
Undoubtedly, import loans provide short-term financing to importers so that they can offer advance payments for goods but delay the actual payment to their bank. This arrangement can be beneficial for businesses that need to maintain inventory levels but lack sufficient available cash to pay the suppliers.
Pre-export loans, however, give the exporters working capital before shipment. The pre-export loans enable exporters to purchase raw materials, manufacture goods, and arrange shipments without waiting for payment from the buyer.
Factoring is a financial transaction in which a business sells its accounts receivable (invoices) to a third party (also known as a factor) at a discount on the face value. Additionally, factoring in international trade:
Specifically, export credits are a common form of financing, which is government-backed financial support provided to local companies to encourage exports. These credits enable exports to get more competitive advantages by making their goods and services more attractive in international markets through favorable financing terms.
The complex network of stakeholders, each of whom is important in enabling international trade. So, who uses it?
SMEs are one of the main drivers to export in global trade. The ability of smaller-sized businesses to access international trade is beneficial and also essential to create promising benefits for international trade. SMEs use global trade finance in order to:
Globally, SMEs face some challenges obtaining affordable trade financing. Those instruments such as letters of credit, export credit insurance, and guarantees provide financing support.
Obviously, corporates generate a high volume of relative trade transactions to control financial flows, streamline operations, and manage risks. These companies might employ integrated financial tools consist of:
Overall, large companies also prefer to work closely with banks, insurers, and export credit agencies to spread involved trade finance activities.
Banks are an integral part of the trade finance ecosystem, which can be seen as an intermediary between importers and exporters. Banks can provide relative services and financial instruments such as:
Of course, banks collaborate with both Export Credit Agencies (ECAs) and Multilateral Development Banks (MDBs) to foster global trade.
Besides the direct users, several other institutions play key supporting roles in the international trade finance including:
Both trade finance and working capital loans provide financing support, but those methods have different aspects to meet the needs of a business:
|
Trade finance |
Working capital loans |
|
Support and streamline international trade transactions |
Cover short-term operational expenses |
|
Specified financial transaction, inherent risk reduction |
General purpose of borrowings |
|
Trade finance instruments |
Business assets |
|
SMEs, corporates, financial institutions |
Businesses need short-term cash flow |
Presently, trade finance platforms are evolving fast, powered by technologies that are reshaping the way businesses access relevant financing support, manage inherent risk, and conduct global trade transactions. So, how technology is transforming trade finance and what does it mean for companies in the global market?
Historically, trade finance was heavily dependent on paper-based management (LCs, shipping documents, invoices) related to banks, customs, insurers, and trading partners. It poses common paper errors, fraud, and delays.
Now, digital trade finance platforms are essential that enhance trade documents and workflows, reducing friction and taking transparency to the next level in the international trade transactions.
Cloud backup solutions
Trade finance platforms are built on the cloud, allowing banks, corporates, and logistics providers to collaborate and share information in real time. Employing trade finance platforms with cloud backup solutions reduces email for sending documents and the negative effects of signing delays.
API integrations
APIs connect platforms with ERP systems, banks, credit insurers, and trade finance tools to enable a seamless exchange of data, making faster and more informed financing decisions.
Artificial intelligence and machine learning
AI is being applied to automate manual process due diligence, fraud detection, and assessing creditworthiness. For example, algorithms can learn from existing data insights and figure out minor errors far more accurately than manual reviews.
Blockchain and smart contracts
Distributed ledger technology is one of the most secure and transparent methods to verify trading transactions. Smart contracts can trigger automatic payments to meet agreed conditions by implementing dispute prevention and speeding up trade cycles.
Electronic know your customer (eKYC) and digital identity
Onboarding international partners process is used to be time-consuming. In due time, platforms offer eKYC tools that verify business identities across jurisdictions quickly and securely.
Trade finance has various benefits, but it also has challenges and considerations. Some of the challenges and considerations include:
Trade finance regulation is increasingly challenging:
These regulations involve extensive resources, which have negative effects on international trade transactions and result in operational costs for businesses engaged in global trade finance.
Integrated solutions:
Modern platforms can deal with these above challenges with:
The trade transaction includes extensive documentation and complicated sub-participation documentary processes, which cause mistakes and take a lot of time:
Digital and automated services and tools reduce involved errors and delays but the need for up-front investment and training.
Integrated solutions:
Therefore, modern trade finance platforms can reduce the friction of paper-based work by offering:
International trade frequently involves working with unknown stakeholders, posing considerable counterparty risk that can negatively affect a company. There are several issues that counterparty risk presents:
Successful counterparty risk reduction requires planning and dealing for banks and financial institutions in the global trade.
Integrated solutions:
Trade finance platforms size counterparty risk through:
Financial products are the lifeline of international trade transactions, which pose foreign exchange (FX) risk to companies. There are the following concerns:
To address these risks, financial instruments such as LCs and currency hedging instruments are needed to make cross-border transactions stable.
Integrated solutions:
Digital solutions can reduce FX risks through:
Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) drive global trade but typically have limited access to trade finance, negatively impacting growth opportunities. There are some challenges faced:
Government-backed refinance programs for trade and new fintech solutions address those challenges in trade finance provision, but most SMEs still face difficulties to access financial services from banks and financial institutions.
Integrated solutions:
Innovative platforms and solutions provide the ability for SMEs to access financial support from formal financial institutions by offering:
Join 1,400+ active users already securing better financing, reducing costs, and making data-driven trade finance decisions. Get started today and stay ahead in an evolving global market.
Unlock Trade Finance Insights
See the Results for Yourself. Sign up to unlock trade finance insights.